Think options are hard to understand? Let me put it simply.
Imagine that you could pay $100 today to guarantee that you could buy a house at a set price — if you commit by a specific date.
- If the market tanks, you lose your $100 — but that’s a drop in the bucket compared to the loss of home value.
- On the flip side, if real estate goes wild, you still have the ability to buy at that locked-in price.
If you understand the example I laid out above, you’ve already got a good handle on basic option trading strategies for beginners.
The above analogy translates well to options trading. Options are contracts that have market values, and traders buy and sell these contracts for profits. Just like trading stocks, option traders speculate whether an asset’s price will be higher or lower by a certain date in the future.
Want to dig deeper? Whether you’re after big moves in an underlying security or seeking a regular income stream, options have something to offer for everyone. Let’s talk about options trading for beginners:
Before we go further, I want to share two recommendations.
First, if you want to trade options, you need a broker. Our top pick is eToro. At $0 per contract and a $100 account minimum, it’s accessible even if you have a small account.
Plus, eToro has thousands of tradable securities, and its user-friendly interface makes it easy to use even for beginners.
But before you start throwing cash around, let me offer up that second recommendation — EDUCATION! This article is a great primer on options basics, but there’s more to learn.
If you want to expand on these lessons, check out the FREE options courses on Option Alpha. They have a variety of free courses for options traders, ranging from beginner to advanced. It’s a great place to learn the ropes before you put money on the line.
eToro is a multi-asset platform which offers both investing in stocks and cryptoassets, as well as trading CFDs.
Please note that CFDs are complex instruments and come with a high risk of losing money rapidly due to leverage. 61% of retail investor accounts lose money when trading CFDs with this provider. You should consider whether you understand how CFDs work, and whether you can afford to take the high risk of losing your money.
This communication is intended for information and educational purposes only and should not be considered investment advice or investment recommendation. Past performance is not an indication of future results.
Copy Trading does not amount to investment advice. The value of your investments may go up or down. Your capital is at risk.
Cryptoasset investing is highly volatile and unregulated in some EU countries. No consumer protection. Tax on profits may apply.
Don’t invest unless you’re prepared to lose all the money you invest. This is a high-risk investment and you should not expect to be protected if something goes wrong. Take 2 mins to learn more
eToro USA LLC does not offer CFDs and makes no representation and assumes no liability as to the accuracy or completeness of the content of this publication, which has been prepared by our partner utilizing publicly available non-entity specific information about eToro.
Now, on to our regularly scheduled programming…
Where to Start: Option Trading Strategies for Beginners
Option trading offers great potential rewards. But with that comes risk. The nice thing is that different strategies come with varying risk levels.
So, before beginning your trading adventure, be sure to first define your goals. Here are some common ones:
- Seeking large returns
- Hedging securities you own
- Selling options for income
From there, it’s time to find a broker and start out on your path. Keep reading to learn how to take the next steps.
What is Options Trading?
Option trading, like short-term stock trading, is most often done in a speculative spirit.
The trader hopes to capitalize on a healthy price move in a short period of time, and to do so much more frequently than a typical buy-and-hold investor would do.
The difference is that while stock investors buy and sell shares of the company, option trading strategies for beginners might include buying and selling option contracts that have rights or obligations to buy or sell shares in the future.
An option trade may last only months, weeks, days or even hours at a time.
One big difference between stock investing and option trading is stocks do not have an expiration date, but option contracts do.
When buying options, the position is considered “long.” There are option traders who sell contracts, which creates a “short” position, too.
While option buyers expect the underlying security to move sharply to profit, sellers collect a credit from the transaction and may hold the position until expiration in order to capture the maximum profit.
Let’s discuss how to get started.
Options Trading for Beginners — How to Get Started
There are four easy steps for trading options for beginners.
- Find a broker.
- Choose a strategy.
- Select your strike price.
- Determine your time frame and exit strategy.
Watch and learn…
Benzinga’s option alert service is one of the best ways to learn about (and trade) options.
It’s a top-rated alert service run by options trader and mentor Nic Chahine.
Not only do you get access to Chahine’s high-conviction and highly profitable options trades, but you also get access to his analysis — so you can understand why he’s making the trade. Here’s what you get:
- High-probability option trades
- Transparent access to trade explanations and analysis
- Market analysis
- Education
In short, it’s a great way to watch, learn, and take action in one fell swoop. Plus, for a limited time, you can get free access to the next Benzinga Boot Camp to learn how to trade stocks and options like a pro.
1. Find an Options Trading Broker
Don’t just go with the first broker you find. Consider these things before you commit:
- Is online or phone support to answer questions regarding the option’s trading platform available?
- Does the broker offer free or paid education to help prepare you?
- Are the commissions and fees competitive?
- What trading tools does the broker offer?
Suggested Options Broker: eToro
eToro created a trading and investing platform to empower traders to gain knowledge and wealth.
Their goal is to help beginner and experienced traders do better in their trading; and they’ve created an investment community built around social collaboration and investor education.
In 2022 eToro launched its eToro Options app, allowing users to explore, learn, and trade options on an easy-to-use and intuitive platform.
A user-friendly interface makes it easy to find all of the tools you need for beginner options trading; low fees and a huge array of tradable assets make it enticing for traders at all levels.
My one complaint about eToro? It doesn’t have a vast library of educational resources. However, if you supplement your brokerage account with a few courses, it can help you fill in the blanks.
eToro securities trading is offered by eToro USA Securities, Inc. (“the BD”), member of FINRA and SIPC. Cryptocurrency is offered by eToro USA LLC (“the MSB”) (NMLS: 1769299) and is not FDIC or SIPC insured. Investing involves risk, and content is provided for educational purposes only, does not imply a recommendation, and is not a guarantee of future performance. https://www.wallstreetzen.com is not an affiliate and may be compensated if you access certain products or services offered by the MSB and/or the BD.
2. Choose a Strategy

Investing in options for beginners begins with basic strategies. Here are four to consider:
- Buy long call options to benefit from rising prices.
- Sell calls against stock shares you own.
- Buy a long put option to benefit from falling prices.
- Sell (short) put options to generate income on stocks.
Let’s explore each of these options strategies for beginners in more detail.
Want to learn even more about these strategies? I already mentioned Option Alpha’s free courses. If you’re looking for more educational resources, consider these two top-rated courses:
- Selling Options for Income: A powerful overview of options trading from an experienced trader
- Udemy’s Option Trading Basics: If you need a primer on the basics, this is the perfect pick
Long Call
A call gives the buyer a right to buy shares of the underlying security at a fixed price on or before a specified expiration date. Long call contracts profit when the security adequately rises in value before expiration.
Whether trading calls or puts options share the following definitions:
- Option premium – the market value of the option (bid/ask).
- Strike price – a fixed price at which the trader might be able to buy or sell shares of the underlying security.
- Expiration – the date the contract expires.
Here’s an example of how you can potentially profit using the long call strategy.
Say you see Apple Inc. (NASDAQ: AAPL) trading at $187. You believe the price will go higher. The image below illustrates the day the call is purchased and then sold.
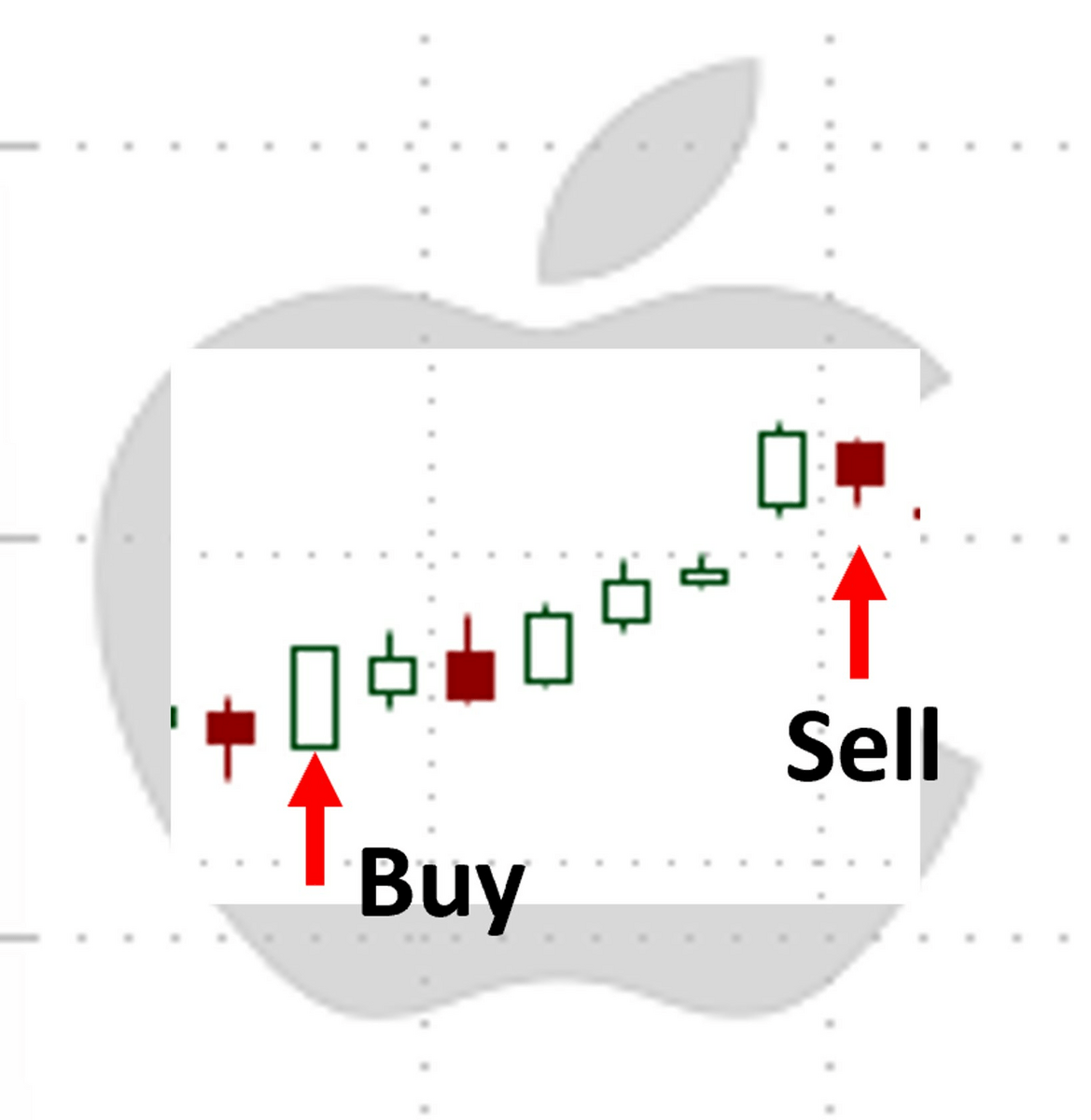
So you buy a $190 call and pay $3 per share. Seven trading days later, you decided to sell the call, which is now valued at $5.50 per share – resulting in an 83% return.
More to know:
- When to use this strategy: When you expect the security’s price to rise.
- Risk and reward: With high reward potential, you’ll find risk as well. For call buyers, the reward potential is unlimited because options continue to gain value as securities rise. Alternatively, the risk associated with buying calls is limited to the investment amount.
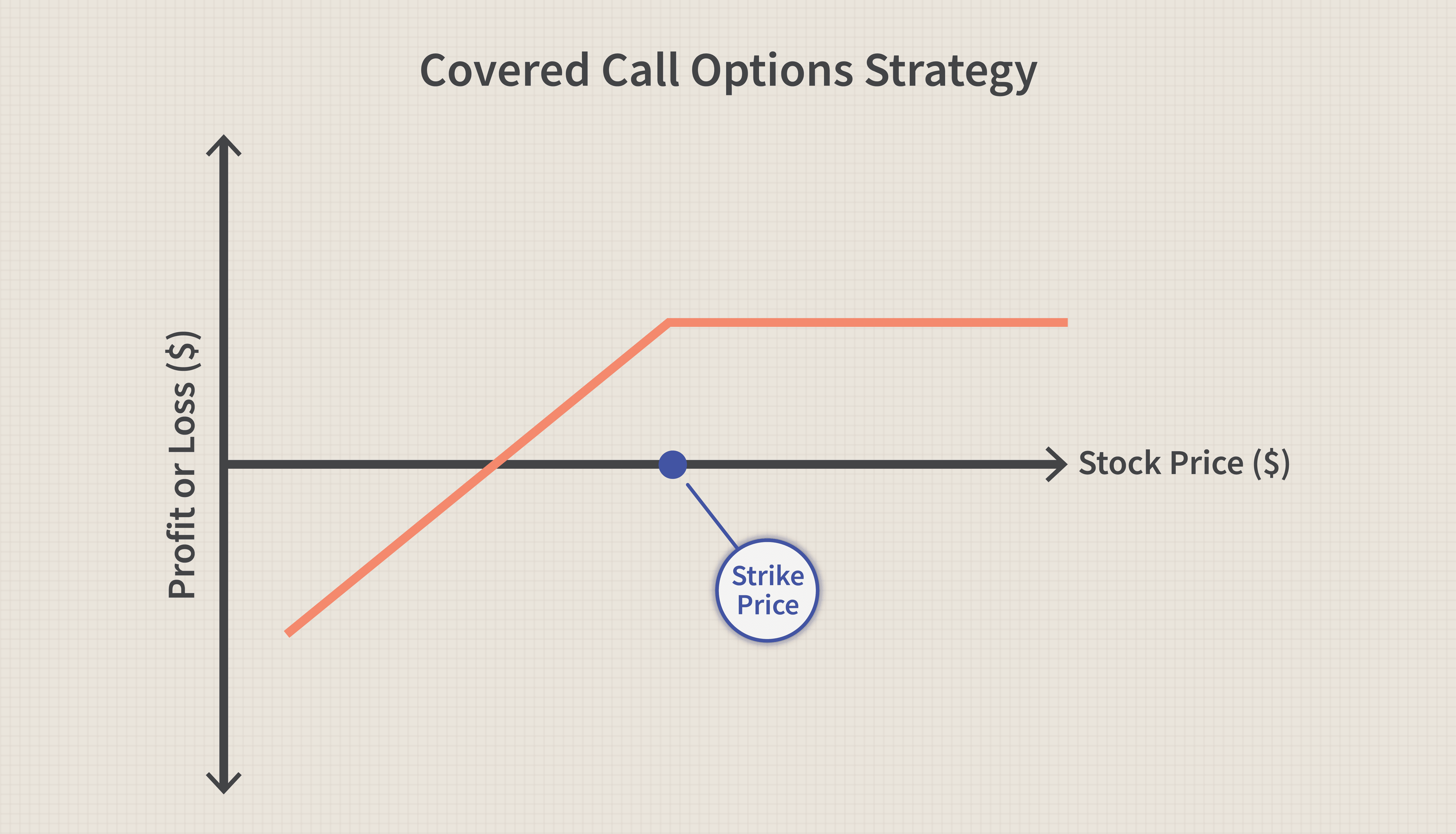
The Covered Call
Selling covered calls is a great option trading strategy for beginners. Let me explain how they work so you can see why.
As a call seller, you receive a credit for the trade, which comes with an obligation to sell shares of the underlying security at a fixed price on or before expiration.
Covered call sellers must have shares in their account. Once purchased, the call being sold against those shares is considered “covered.”
If the underlying security is trading above the strike price at expiration, the call is considered “in-the-money,” which means shares of the security will trade hands.
On the other hand, if the security trades below the call strike price by expiration, the call will expire worthless and no shares are exchanged.
Consider this example:
Once again using Apple Inc. (NASDAQ: AAPL) as an example, suppose you purchase 100 shares at $187, and now sell the $190 call for $3 per share.
As the call seller, you have an obligation to sell shares at $190 at expiration if AAPL trades above $190.
At expiration Apple trades at $192, so you are obligated to sell shares for $190.
More to know:
- When to use this strategy: Option trading for beginners may start with selling calls against shares for income. There are two outcomes to this strategy – you might keep the credit received and the shares, or you might keep the credit and lose the shares at expiration.
- Risk and reward: Selling covered calls is a low-risk option strategy. The credit received when selling the covered call is the most the trader will earn on the option, but there is a risk of losing the shares as well.
- In our trading options basic scenario, the shares were called away. You bought shares for $187 but were required to sell them for $190, which translated into a $3 gain on the stock investment. But a credit was received earlier for $3 per share. So, in total, as a covered call seller, you gained $6 per share (although you gave up the shares).
Long Put
Put contracts may feel counterintuitive at first.
When purchased, puts are considered “long” positions. While long calls profit from rising prices, put contracts profit when prices fall.
Buying put contracts gives you as the buyer a right to sell shares at a fixed price on or before an expiration date, but owning shares is not required before buying puts.
To illustrate, let’s again consider Apple Inc. (NASDAQ: AAPL).
This time, AAPL is trading at $153 and is expected to fall in the near future.
The illustration below shows when the put was purchased and sold:
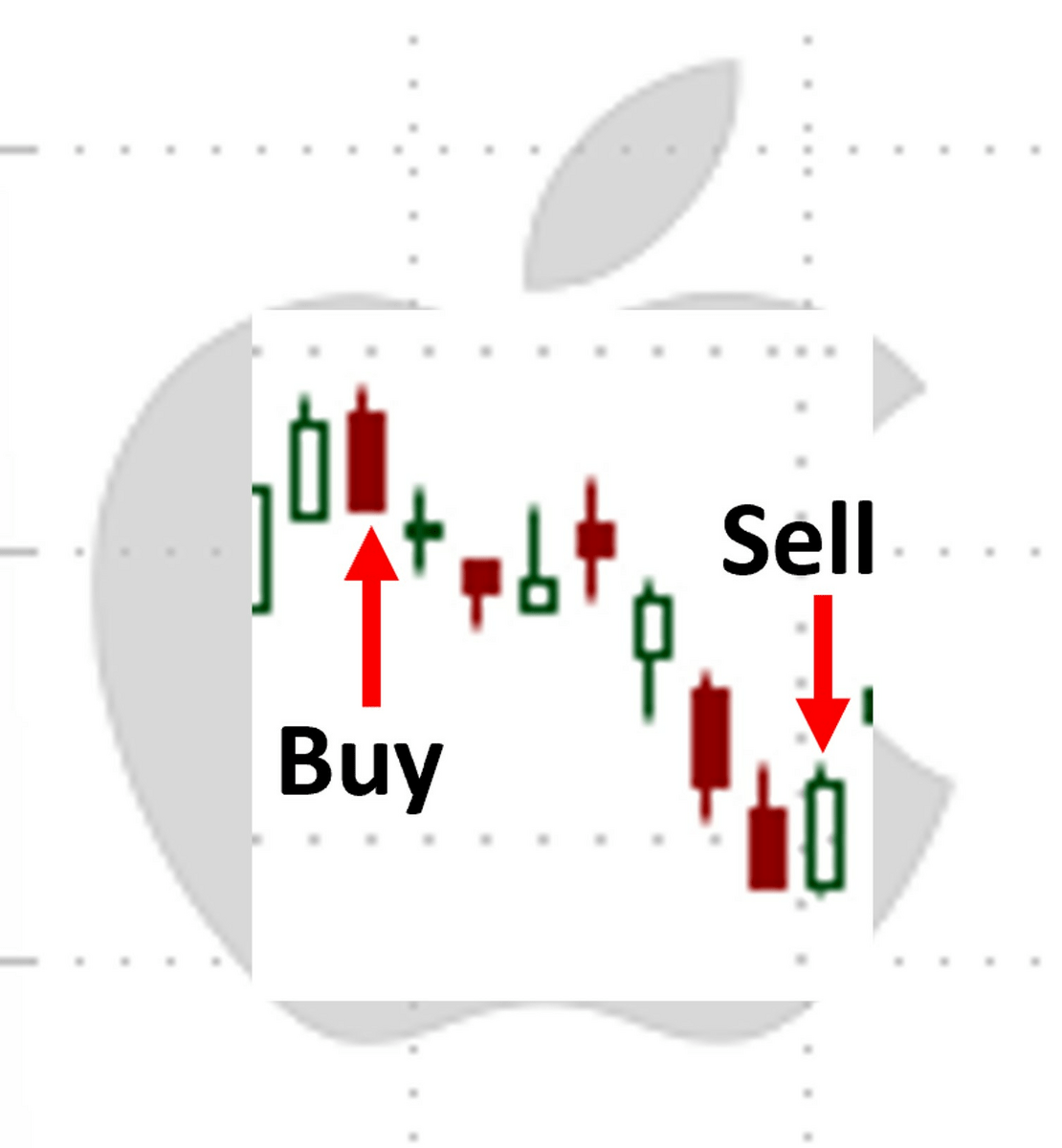
Expecting weakness in the stock, you purchase a $152.50 put contract for $6.75 per share. Eight trading days later, believing the stock might rise – going against the put trade – it is sold at the current market value of $12 per share.
After subtracting out the purchase price, you profit $5.25 per share, providing a 78% return over eight trading days.
More to know:
- When to use this strategy: From this example, put contracts gain in market value as the underlying security declines. As an option trader, you buy put contracts to profit when stock prices are expected to fall.
- Risk and reward: Long puts are capable of losing 100% of the investment amount. In our example, the risk was $6.75 per share. Long puts can continue to gain value until the security reaches zero dollars in market value.
Short Put
Selling put contracts creates a “short” position and benefits as stock prices rise in value.
Since buying puts gives the trader a right to sell shares of stock, selling puts creates an obligation to buy shares.
Therefore, put sellers may have one of two objectives:
- Collect a credit by selling puts, or
- Using the put to acquire shares of a security.
Here’s an example.
Say you’re interested in buying shares of Apple Inc. (NASDAQ: AAPL), at a later date (the option expiration).
If AAPL is trading at $153 today, you might sell the $152.50 put for a credit of $6.75. One of two outcomes will occur depending if AAPL trades above or below the $152.50 strike price.
- At expiration, if AAPL trades above $153, the contract expires worthless and you as the seller have profited $6.75.
- Alternatively, if AAPL trades below the strike price it will be exercised.
More to know:
- When to use this strategy: Selling long puts is appealing to traders who wish to generate income or are hoping to acquire shares of the security at a lower price than the current market value.
- Risk and reward: The maximum profit when selling puts is the credit received. Traders run the risk of having to buy shares of the underlying security with this strategy, and the broker may require all or part of funds necessary to acquire shares of the security. Check with your broker to determine the account requirement before selling puts.
- Trading options for beginners may also include buying and selling options together – spread trading.
Bonus: Vertical Spread with Calls
A vertical spread is created by buying and selling a call with the same expiration but different strike prices.
Here’s an example using Apple Inc. (NASDAQ: AAPL):
Type of Spread | Long Call Spread |
|---|---|
Strike Price | Bought/Sold/Price |
$180 Call | Sell for $1.30 |
$175 Call | Buy for $4.60 |
Cost of Trade | Net Debit $3.30 |
Vertical spreads can lower the cost and risk of trading calls, but it also limits the reward.
In the example, had you as the trader purchased the $175 call independently, the investment and risk would have been $4.60 per share, having unlimited reward.
However, to offset costs, you could sell the $180 call.
By choosing the vertical, you as the investor have limited reward no matter how strong the security moves in the desired direction.
More to know:
- When to use this strategy: An alternative to buying a single call, trading a bullish vertical can lower the cost of the trade, although reward is limited.
- Risk and reward: The risk of a debit vertical spread trade is capped by the debit paid. The reward is limited to the difference between the two strike prices, $5 in our example, minus the debit paid. The risk for this AAPL vertical is $3.30. Subtracting this debit from the difference in strike prices, $5, yields a reward of $1.70 per share.
3. Set Your Strike Price
After becoming familiar with option strategies, the next step is to set your strike price.
For strike selection, a general rule of thumb is to start with the at-the-money contracts (strike closest to the current stock price) or select a strike price based on your target for the underlying to reach.
This can be accomplished by using technical indicators in your analysis. Indicators such as the Average True Range (ATR), Bollinger bands, or Keltner Channels, could help you set your targets.
To explore this topic and more in greater detail, check out Option Alpha’s FREE courses
4. Determine Your Time Frame
Finally, determine your time frame.
When buying options, you should have an idea of the timeframe it might take the security to make the anticipated move.
Doing so helps you determine how much time you’ll need for the contract. Be sure to buy options out in time to allow for the full anticipated move to occur.
The amount of time you need will depend on how often you want to make similar trades. If you want to make a new trade every week, then you’ll want to buy two weeks.
A simple rule of thumb is to add at least one week to one month more than you need for the move to occur.
Benefits of Trading Options
As seen in our call and put examples above, options can be rewarding — plus, they can be traded for a fraction of the cost to acquire shares of the security.
While there are many different strategies available for option trading, almost all of them reduce the amount of capital necessary to participate.
Options trading provides the potential for greater returns than buying the security outright because the option contract is priced only for the opportunity of owning or selling shares within a given period of time.
Because they are lower in price, a small change in the underlying stock price can make a profound difference in the option price.
For example, an option for owning 100 XYZ shares at a strike price of $50 might cost $5.00 per share (or $500 total).
By comparison, the price of owning the shares outright would cost $50,000. If the price of XYZ were to rise by $5 the next day, the value of the shares would be $55,000 (a 10% increase).
By contrast, the price of the option might increase to $10 per share (or up to $1000 total value of the option contract). This would be a 100% increase in the option price.
Are Option Alerts Services Any Good?
You may consider alert services when trading options basics. Option alert services can help you trade with less personal research. A good rule of thumb is to find out the trading results of any alert service.
The Best Option Alert Services
Alerts can shorten the learning curve of options trading for beginners. Here are some top-tier services to consider:
Benzinga Options
Benzinga Options shares its star trader’s high-conviction and highly profitable trades directly to your email and SMS inbox.
The alerts include a complete explanation and analysis so you can learn how to replicate your own trades. One or more trades are given each week and a variety of strategies.
This takes a bit more learning to get up to speed, but the service is geared for beginners willing to learn along the way.
The Trading Analyst
The Trading Analyst uses a Volume Confirmation Algorithm to help reduce incidences of losing trades. They offer trade potential of 100% profits.
Better yet, The Trading Analyst offers options trading for beginners. These are typically call option recommendations given at the rate of two to five per month. If you want to speed up your learning curve, I highly recommended this service.
Mindful Trader
Mindful Trader is designed to help traders identify profit patterns that come along, when they come along.
This service highlights trades that have a quantitative edge. These are simple trade recommendations on calls or puts. Trades are usually given every day, sometimes more than one. The trades usually last no more than a week.
Must-Know Tips for Investing in Options for Beginners
Option trading is exciting for the reward potential, but there are a wide variety of strategies to choose from.
Be sure to write down these tips to help you get started with confidence:
- Select a broker that has the tools and support to help you be successful.
- Utilize free or paid services for education about the rights, obligations, risks and rewards of option trading.
- Have a start-to-finish game plan for trading options.
- Practice – trade on paper or in small quantities to get started
More must-have resources for options traders…
- A brokerage account. Our top pick is eToro.
- Great charting software. Our top pick? TradingView.
- Trading alerts. Our top pick? Benzinga Options.
Plus, check out our article about the best options trading analysis software.
eToro is a multi-asset investment platform. The value of your investments may go up or down. Your capital is at risk.
Final Word: Options Trading for Beginners
You may find option trading to be intimidating at first, but take it one step at a time to build confidence.
Once you understand the basics, including the risks, rewards and risk management, trading them can be fun and rewarding.
WallStreetZen has expanded into stock-picking!
With a Zen Investor subscription, you can save precious research time and let a 40+ year market veteran do the heavy lifting for you. Here’s what you get:
✅ Portfolio of up to 30 of the best stocks for the long haul, hand-selected by Steve Reitmeister, former editor-in-chief of Zacks.com with a 4-step process using WallStreetZen tools
✅ Monthly Commentary & Portfolio Updates
✅ Sell Alerts if the thesis changes
✅ Members Only Webinars
✅ 24/7 access to all the elements noted above
✅ Access to an archive of past trades and commentary.
FAQs:
What is the best strategy for options trading?
The best strategy for option trading is to identify a broker that offers tools, support and online training for you as a new trader. Once you’ve identified which broker to use, begin your training and prepare yourself for the first option trade.
Which trading option strategy is best for beginners?
The option trading strategy that is best for beginners is selling covered calls. This strategy is considered one of the safest and is a great way to introduce a new trader to options trading.
What are the 4 option strategies?
The 4 main option strategies are:
1. Buying Calls
2. Selling Covered Calls
3. Buying Puts
4. Selling Puts for Income
Where to Invest $1,000 Right Now?
Did you know that stocks rated as "Buy" by the Top Analysts in WallStreetZen's database beat the S&P500 by 98.4% last year?
Our July report reveals the 3 "Strong Buy" stocks that market-beating analysts predict will outperform over the next year.