These days, everyone and their grandma seems to be throwing around terms like “artificial intelligence,” “algorithms,” and “systematic trading.” Unfortunately, these terms are often tossed around far too loosely and interchangeably.
This article seeks to change that. By the end, you’ll clearly understand the buzzwords that have infiltrated everyone’s lexicon in 2025.
More importantly, you’ll learn the multiple ways traders leverage lucrative systematic trading approaches that can compete with even the best discretionary fund traders.
Prefer to use someone else’s system? Try Stock Market Guides.
Stock Market Guides is a stock and options trading alerts service that scans for trade setups and sends you alerts in real-time. The software scans for trades based on numerous trading strategies which have been rigorously backtested through years of research and statistical analysis.
As a subscriber, you get trade alerts based on historically-profitable setups. These strategies generated a 79.4% annualized return on nearly 300,000 backtests (for stocks) and 150.4% annualized return in backtests (for options).
Introduction: What Is Systematic Trading?

Systematic trading, also known as quantitative trading, refers to a method of defining trade objectives, risk constraints, and rules that can be tested and followed algorithmically.
When you think of systematic strategies, you probably think of complex algorithms supported by the latest supercomputer. While this is often the case, systematic trading can also take a far simpler approach and be managed manually by humans alone.
While systematic trading and algorithmic trading are often used interchangeably, there is a difference. It’s more accurate to think of systematic trading as a set of trading rules, whether simple or complex.
Algorithmic trading, on the other hand, generally refers to a systematic approach supported by powerful supercomputers.
As you might imagine, the right computer is crucial to systematic trading success.
Our top pick? The Radical X13 EZ Trading Computer.
Here’s why we love it.
- It includes a liquid-cooled Intel Core i9-13900KF 24 CORE Processor @ 5.8 Ghz In Turbo Boost Mode.
- Option to include 64 GB of RAM.
- Available 1 TB solid state drive (SSD).
- Ability to display up to 4 monitors.
Systematic vs. Discretionary Trading
While systematic trading requires predetermined strategies and models to execute trade decisions, discretionary trading involves making decisions based on intuition and subjective judgment.
In other words, discretionary traders make decisions based on their analysis, experience, and market perception.
Systematic Trading: Pros and Cons
Advantages of Systematic Trading
- Emotionless: Following predefined rules removes the emotional component from trading.
- Consistency: A rules-based approach ensures trades are executed consistently.
- Scalability: Systematic strategies are much easier to scale.
- Backtesting: This approach allows traders to backtest strategies before trading actual capital.
Disadvantages of Systematic Trading
- Model Risk: If the systematic approach algorithm is based on flawed assumptions, it could lead to poor trading outcomes.
- Overfitting: If a model is too finely tuned to past data, it may perform poorly in real-world conditions.
- Inflexible: Systematic trading strategies cannot easily adapt to changing market conditions unless they are anticipated and built into the rules beforehand.
Discretionary Trading: Pros and Cons

Advantages of Discretionary Trading
- Flexible: Discretionary fund traders can quickly react to new information and evolving market conditions.
- Human Intuition: Discretionary trading allows qualitative insights and experience to be applied when needed. Put another way, discretionary traders can act on ‘gut feelings.’
- Tailored Approach: Discretionary trading mandates can be adjusted to specific market conditions or assets.
Disadvantages of Discretionary Trading
- Emotional Bias: Discretionary fund traders are prone to emotional decisions. This can lead to impulsive trading or maintaining a position longer than is warranted.
- Lack of Consistency: Emotions and mental states can drive different results. Depending on a trader’s health or other personal factors, for example, performance may be impacted.
- Limited Scalability: Unlike systematic trading, applying the same discretionary decisions across many trades can be challenging.
Systematic Trading Strategies
BONUS: Need to hone your coding skills?
While many programs can help with pre-coding algorithms, your odds of success are far higher if you understand coding basics.
Skillshare is an educational hub that’s loaded with courses on coding — including Coding 101: Python for Beginners, a course that guides you from the basics to more advanced coding strategies with one of the most popular programs for creating trading algorithms.
Plus, you can get started with Skillshare for FREE! Check out the catalog now.
Trend Following
Trend following is based on the assumption that prices tend to move in trends over specific timeframes. Once established, a trench is more likely to continue than reverse, according to this approach.
Traders identify trends using a variety of technical indicators, like moving averages and break patterns, to identify the direction and strength of the trend.
Once recognized, they take positions consistent with the trend, maintaining them until a reversal signal is established.
Trend following relies on charts. Need a great charting platform? Our top pick is TradingView.
Charting is the main attraction for TradingView’s 30+ million users (yes, it’s the most popular trading website in the world). Your toolkit will include:
- 14 chart types
- 20+ timeframes
- 90+ drawing tools
- 100+ pre-built indicators
- 100,000+ community-built indicators
- 70+ exchanges from 50+ countries
Pro+ costs $24.95/month when billed annually, but our link below will give you a 30-day free trial:
Unlike value investing, Trend Following does not focus on an asset’s fundamentals. Instead, successful use of this method hinges on identifying price directions, managing risk, cutting losses early, and letting profits accrue.
While some trend-following traders experience frequent small losses, larger profits from strong trends can still ensure the strategy is profitable.
- Implementation: An example of Trend Following using a systematic approach would be a rule that triggers the purchase of shares of a stock if the price crosses a certain threshold.
For example, a buy might be triggered when the stock price crosses above the 200-day moving average. This would represent the entry price. This systematic approach would also include an exit strategy. For example, perhaps the rule would dictate that the shares should be sold once they rise three percent to lock in profit. There may also be a rule to avoid substantial losses (i.e., sell shares if the stock price drops two percent or more).
Mean Reversion
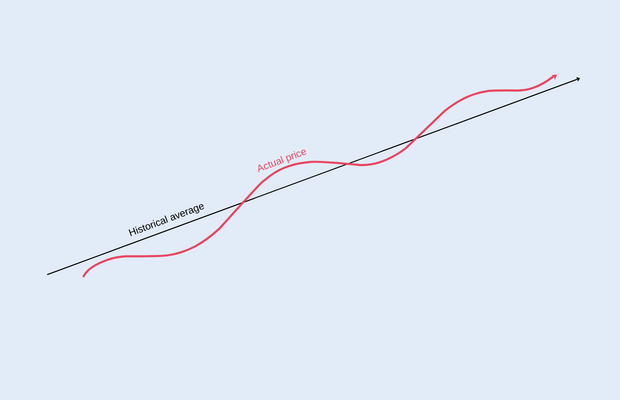

Mean Reversion assumes that assets tend to oscillate around an average – or mean – value over time. When asset prices deviate substantially from their historical average, this might indicate that a security is becoming overbought or oversold.
- Overbought: When an asset is becoming overbought, this might indicate its price direction is about to reverse and fall. Mean Reversion traders would take a short position in the security.
- Oversold: When an asset is becoming oversold, this might indicate its price direction is about to reverse and rise. Mean Reversion traders would take a long position in the security.
To help identify reversion to the mean, technical tools like Relative Strength Index (RSI) are leveraged. RSI is a metric that assesses the speed and change of price movements. If RSI is high, it implies a stock is overbought (and could soon fall). Alternatively, If the RSI is low, it implies a stock is oversold, indicating a potential price bounceback.
While the method can be effective, it’s not perfect. Not all price deviations will revert. At times, market conditions or fundamentals can materially affect prices for sustained periods.
- Implementation: A systematic trading approach using mean reversion could trigger a buy when the RSI crosses below a certain threshold, and a sell rule could be created for when the RSI crosses above a certain threshold.
Statistical Arbitrage
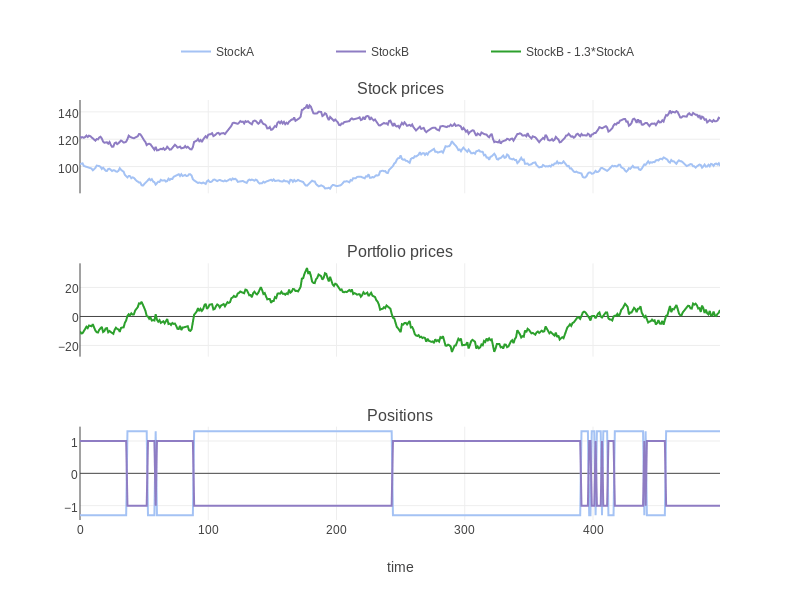
Statistical Arbitrage, or StatArb, is a quantitative trading method. Traders use complex mathematical models and algorithms to look for statistically significant mispricings or patterns across different securities.
Typically, traders will hold multiple positions across a wide range of assets. Ultimately, they’re attempting to profit off small price inefficiencies.
As a result of the large quantities of data that need to be parsed, Statistical Arbitrate relies heavily on sophisticated software and powerful computational power.
- Implementation: To use StatArb with a systematic approach, a trader could set a rule to identify deviations from the established relationship between multiple assets. When a significant enough deviation occurs, a short could be triggered on the outperforming assets with a simultaneous long on the underperforming assets. When the deviations subside sufficiently, the trades could be unwound.
Pairs Trading
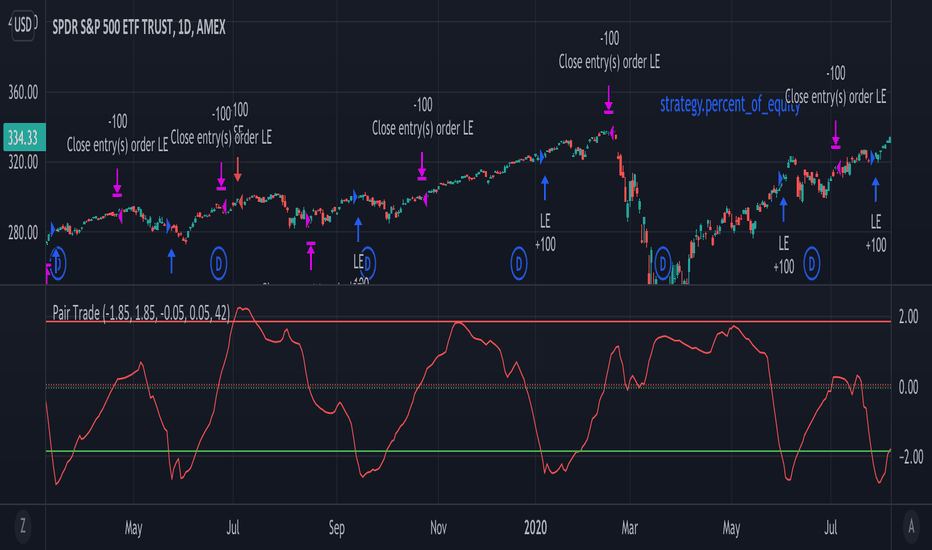
Pairs Trading is a form of Statistical Arbitrage with nuance. Instead of holding numerous assets simultaneously, Pairs Trading focuses on just two securities.
Traders identify two assets with historically strong correlations. Then, they look for periods where this historical correlation breaks down. For example, instead of moving in unison, one asset might rally while the other falls. Since the trader knows they are historically correlated, they expect the prices to revert to their historical norm.
As a result, a trader that identified this weakening correlation would take a long position in the falling security and a short in the appreciating asset.
Again, the assumption is the two names will revert to their historical relationship, breaking this temporary divergence.
- Implementation: A systematic approach to Pairs Trading would look similar to StatArb but with only two assets. When the assets deviate sufficiently from their historical relationship, a rule will trigger a buy of the underperforming asset and a sell of the outperforming one.
Market Making

Market Makers are an integral component of functioning capital markets. They help generate liquidity in the market by consistently offering to buy and sell securities, helping drive smoother trading.
Market Makers seek to profit from the buying and selling of securities. They benefit from the difference (spread) between bids and asks. Essentially, they retain the difference between the purchase price of a security and its sale price.
- Implementation: A systematic trading approach using market making would entail continuously quoting buy and sell prices for a security, aiming to profit from the bid-ask spread. The approach would demand constant quote adjustment based on real-time market conditions..
Momentum Investing
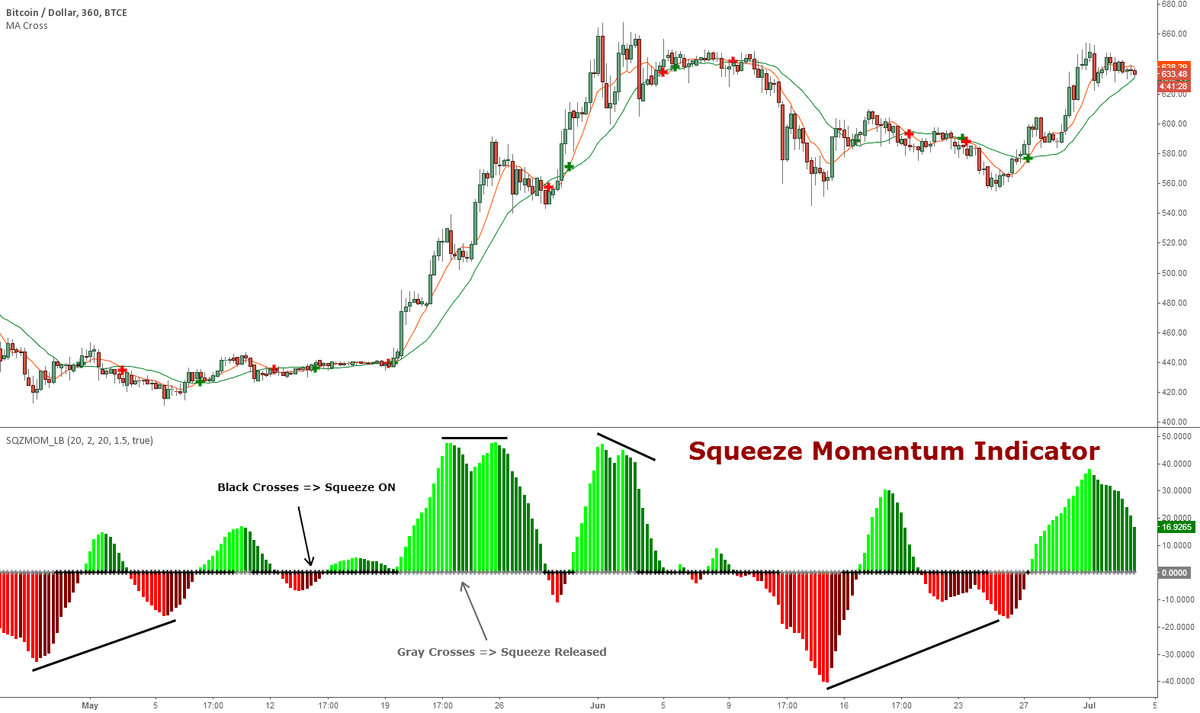
Momentum Investing is a simple systematic approach algorithm. It rests on the following premise:
- Assets that have risen in price recently will likely continue to rise.
- Assets that have fallen in price recently will likely continue to fall.
Typically, momentum traders will identify and buy assets showing strong recent performance in the hopes the trend will continue. Momentum traders often use technical tools like relative strength indices to help identify strong contenders.
Momentum trading is heavily rooted in behavioral finance. It relies on the fact that markets may not be perfectly efficient and that price trends can persist for some time.
- Implementation: An example might be an approach that ranks a group of securities each month, identifying the top five performers. The rule would trigger a buy of these stocks, assuming that recent strong performance will persist. The ranking would be renewed each month, rebalancing (buying and selling) as required.
High-Frequency Trading (HFT)
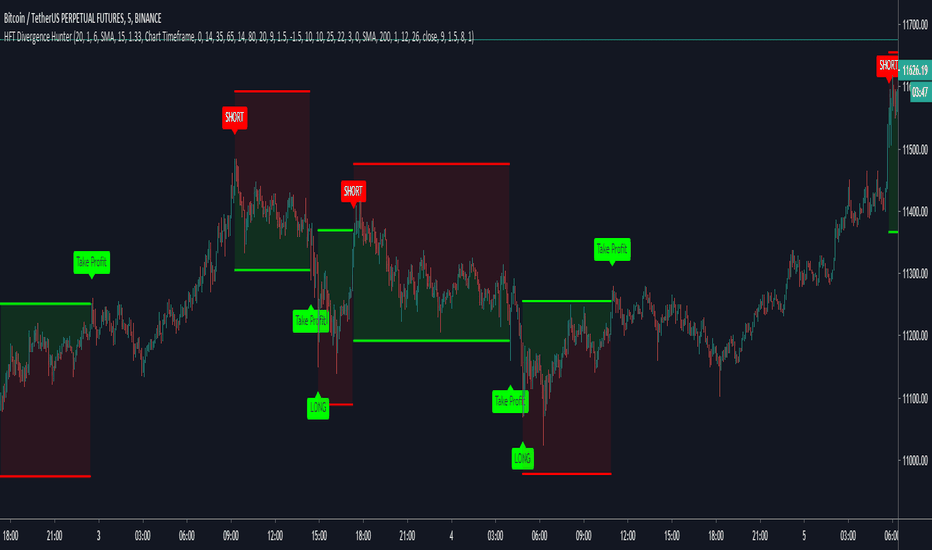
High-frequency trading is a modern systematic strategy. It’s an evolution of algorithmic trading that has taken individual execution down to milliseconds or even microseconds.
HFT strategies look to exploit small inefficiencies in the market. Leveraging large pools of capital, profit is derived by combining vast numbers of small trades.
HFT algos rapidly parse market data, making investment decisions based on rapidly changing prices, order flows, and other conditions.
While HFT can perform a similar role as traditional market makers by driving liquidity, they’ve also been criticized for exacerbating volatility and creating an unfair playing field.
- Implementation: This approach requires an algorithm that executes large numbers of trades in fractions of a second. For example, the algo may follow mean reversion but at very high volumes and speed.
News Trading

This method entails acting quickly on market-moving news, like an earnings result announcement. By acting swiftly, traders using this approach can profit from short-term volatility.
News releases, like decisions from a central bank, can cause significant swings in asset prices. Some traders will follow these critical stories manually, while others will leverage automated systems that look for specific keywords.
Given the pace at which markets move in modern times, a news trading strategy typically demands rapid decision-making to realize profits.
- Implementation: In terms of implementation, a systematic trading approach to trading on the news is perhaps the most complex. This approach leverages Natural Language Processing (NLP) to analyze and identify sentiment on, for example, social media. A simple rule might generate a buy of a broad market ETF if the market sentiment on X is particularly high. The exact definition of what “high” is will vary between models. For example, it might trigger a buy if 80% of the social media sentiment is bullish on the stock market.
If you ultimately want to create algorithm scentered around news stories, it’s crucial to get an understanding of what types of news events have the power to move stock prices.
To get a feel for news that can move stocks, we highly recommend Seeking Alpha.
Seeking Alpha is a site that crowdsources investment research written by more than 16,000 contributors, all of whom are required to disclose their portfolio holdings. It features a diverse array of opinions and investing approaches that make it an invaluable resource for investment due diligence.
Plus, if you use the link below you can get a FREE 7-day trial, plus $50 applied to any subscription you choose to pursue after the trial period.
(Read our full Seeking Alpha review for more info)
The Role of Machine Learning and AI
caArtificial intelligence possesses the potential to disrupt the systematic trading space substantially. Leveraging computation power, pattern recognition, and the ability to analyze huge amounts of data, AI is revolutionizing the financial landscape.
Here are several ways AI can be used to gain an advantage in systematic trading:
Data Processing & Analysis
- Artificial intelligence can identify patterns in data that may be beyond the capabilities of a human analyst.
Feature Engineering & Selection
- AI can help identify new variables from raw data that can then be used to improve price movement predictions.
Model Optimization
- Trading models can be optimized automatically by AI over time. As new data emerges, it can adaptively alter current strategies.
Risk Management
- Complex risk scenarios can be modeled much more easily than before. This provides traders with a better understanding of the downside potential.
- Risk can also be managed by optimizing asset allocations. AI can perform the resource-intensive tasks of considering transaction costs and other market frictions.
Alternative Data Analysis
- AI can parse vast quantities of both structured data (i.e., figures taken from a clean spreadsheet) and unstructured data (i.e., sentiment based on social media posts from a particular date) at speeds unattainable by humans. Put another way, AI can identify insights that might not be available from conventional financial data.
High-Frequency Trading
- AI algorithms can support the high speeds needed to identify and act on rapidly fleeting market opportunities.
Adaptive Strategies
- AI can leverage machine learning to continuously adapt to changing market conditions.
- Models can be trained to adapt to specific market environments, such as bull markets.
Reduction of Human Bias
- Artificial intelligence can remove the emotional and cognitive biases present in human traders. Appropriately designed, AI can operate free from these biases, leading to more consistent results.
Backtesting & Simulation
- AI can speed up backtesting, enabling far more comprehensive analysis to occur.
- Various strategies can be tested against the backdrop of numerous market conditions.
Sentiment Analysis
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) techniques can be leveraged to analyze financial reports, social media, news articles, and other sources. Market sentiment can be gauged in the analysis, helping drive more informed investment decisions.
Market Prediction
- Forecasting models can be built to help predict future asset price movements.
How to Get Started with Systematic Trading
The right tools can help improve your odds of success with any type of trading, but it’s particularly true with a tech-reliant method of trading like systematic trading.
TradeStation – Best Overall Algo Trading Platform
TradeStation is my favorite platform for implementing sophisticated and lucrative algorithms. While it has the potential for complex models, its user interface is straightforward.
TradeStation even possesses canned systematic trading approaches. After activating a Chart Analysis window on the platform, you can select your desired pre-programmed strategy from the menu bar and start your systematic trading approach instantly. If you’re curious about the exact steps, check out this help page from TradeStation.
In short, this powerful platform is suitable for beginners and advanced traders alike.
TradeStation has an impressive thirty-plus-year history. The platform stands out with hundreds of customizable apps, competitive commissions, and access to a massive library of educational materials and research.
Finviz – Best Platform for Backtesting and Advanced Visualizations
When testing your algorithm on historical, real-world data, no better platform comes to mind than Finviz. Whether you’re a beginner testing out a new model or a seasoned vet looking to refine an existing one, Finviz offers a safe place to trial and assess systematic trading approaches.
With Finviz Pro, users gain access to a vast set of tools, including:
- Backtesting that can recognize 102 unique chart patterns up to two years back using multiple combinations.
- 67 stock screening metrics.
- Integrated news aggregation.
In addition to real-time quotes, charts, backtesting, and email alerts, Finviz also offers heatmaps that provide valuable sector and industry visualizations.
Radical X13 EZ Trading Computer – Best Algo Trading Hardware

If you’re looking to run an automated, lucrative algo, you need the proper hardware on your side. One of the best computers suited to this task is the Radical X13 EZ Trading Computer.
Here’s why we love it.
- It includes a liquid-cooled Intel Core i9-13900KF 24 CORE Processor @ 5.8 Ghz In Turbo Boost Mode.
- Option to include 64 GB of RAM.
- Available 1 TB solid state drive (SSD).
- Ability to display up to 4 monitors.
The Radical X13 also comes with an impressive 5-year warranty and lifetime tech support.
Review: Must-Haves for Systematic Trading
To get a leg up as a systematic trader, you need the right tools. Here are some of our top resources:
Best algo trading platform | |
Best program for advanced backtesting | |
Computer | |
Coding course |
Final Word:
Systematic trading can take on multiple forms. Traders commonly use supercomputers and advanced software to implement known strategies, like Statistical Arbitrage or High-Frequency Trading. While similarities and overlap exist, each strategy is unique and focuses on different market aspects.
Advancements in artificial intelligence are only accelerating improvements in systematic trading. Machine learning and AI increasingly play a pivotal role by offering rapid data processing, pattern recognition, model optimization, sentiment analysis, and more.
All this while reducing inefficiency, lowering errors, and cutting out emotional biases.
For those looking to venture into systematic trading, platforms like TradeStation and Finviz stand out as some of the most impressive and accessible options available. With these tools, traders can backtest their very own algorithm from the comfort of their homes.
FAQs:
How do I become a systematic trader?
One way to become a systematic trader is to leverage platforms like TradeStation to build lucrative algorithms. Before embarking, ensure you backtest your model and identify any potential shortfalls or risks.
Is systematic trading better?
Systematic trading or a systematic approach algorithm is often considered superior to discretionary trading since it takes a disciplined, consistent, and unemotional approach to investing.
What is systematic vs algo trading?
Systematic trading refers to a rules-based trading strategy that may or may not involve sophisticated software (systematic approach algorithm). Algo trading specifically refers to executing pre-defined trading instructions automatically, typically supported by powerful computers and advanced software.
What is the role of a systematic trader?
The role of a systematic trader is to design trading rules that can be implemented clearly without discretion. That is, systematic traders provide instructions that can be followed without any subjectivity needed.
Where to Invest $1,000 Right Now?
Did you know that stocks rated as "Buy" by the Top Analysts in WallStreetZen's database beat the S&P500 by 98.4% last year?
Our July report reveals the 3 "Strong Buy" stocks that market-beating analysts predict will outperform over the next year.