Top 3 Tips: Dividend Investing For Beginners
- Quality over yield: Don’t just chase the highest dividend percentages. Use tools like WallStreetZen’s Dividend Stock Screener to find companies with sustainable payout ratios and steady cash flow.
- Reinvest automatically: Turn on dividend reinvestment (DRIP) so your payouts buy more shares and compound over time without extra effort.
- Diversify for stability: Build your income stream across sectors like consumer staples, utilities, and healthcare using WallStreetZen’s Zen Ratings to compare fundamentals and risk.
Why Explore Dividend Investing?
You want to build wealth while earning regular income from your investments. You’ve heard about dividend investing, but you’re not sure where to start or how to identify the best dividend-paying stocks.
Dividend investing is one of the most powerful wealth-building strategies available. In this guide, I’ll walk you through dividend investing for beginners, from understanding dividend yields and payout ratios to finding quality dividend stocks using proven screening methods.
By the end of this article, you’ll understand what dividend investing is, how to calculate key metrics like dividend yield, and how to build a sustainable dividend portfolio that can provide you with monthly passive income for years to come.
Let’s dive in.
What is Dividend Investing?
Dividend investing is a strategy where you focus on buying stocks of companies that regularly pay dividends — cash payments made to shareholders as a reward for owning the stock. Instead of relying solely on stock price appreciation, dividend investors prioritize companies that consistently return a portion of their profits directly to shareholders.
Think of dividends as your share of a company’s success. When you own dividend-paying stocks, you’re essentially getting paid to own pieces of profitable businesses. These payments typically come quarterly, though some companies pay monthly dividends. Here’s a screenshot of my Public account, where I hold a variety of stocks as well as the index fund VTI — I receive dividends from a variety of my holdings.

A $5 or $10 dividend here and there may not feel like a lot, but over time, it can snowball. Over the past 1.5 years, I’ve received over $600 in dividends with an account size of about $15K.
The beauty of dividend investing lies in its dual benefit: you earn regular income from dividend payments while potentially benefiting from stock price appreciation over time. This combination has historically made dividend stocks less volatile than growth stocks, while still delivering competitive long-term returns.
Why Dividend Investing Works for Building Wealth
Dividend investing has proven its effectiveness over decades, though performance varies by time period and methodology. The S&P 500 Dividend Aristocrats — companies that have increased their dividends for 25+ consecutive years — have delivered competitive total returns to the broader market with notably lower volatility in recent decades.
Here’s what makes dividend investing particularly powerful:
Compound Growth Through Reinvestment: When you reinvest your dividends, you buy more shares, which generate more dividends, creating a snowball effect. (Related reading: The Best Compound Interest Investments in 2026)
Market Volatility Buffer: During market downturns, dividend payments provide steady income even when stock prices fluctuate.
Understanding Dividend Yield: The Foundation of Analysis
Before you can evaluate dividend stocks effectively, you need to understand dividend yield — the most basic metric in dividend investing.
How to Calculate Dividend Yield
Dividend yield shows you how much income you’ll earn for every dollar invested. Here’s the simple formula:
Dividend Yield = Annual Dividend Per Share ÷ Current Stock Price
For example, if a stock pays $2.00 annually in dividends and trades at $50 per share, the dividend yield is 4% ($2.00 ÷ $50.00 = 0.04 or 4%).
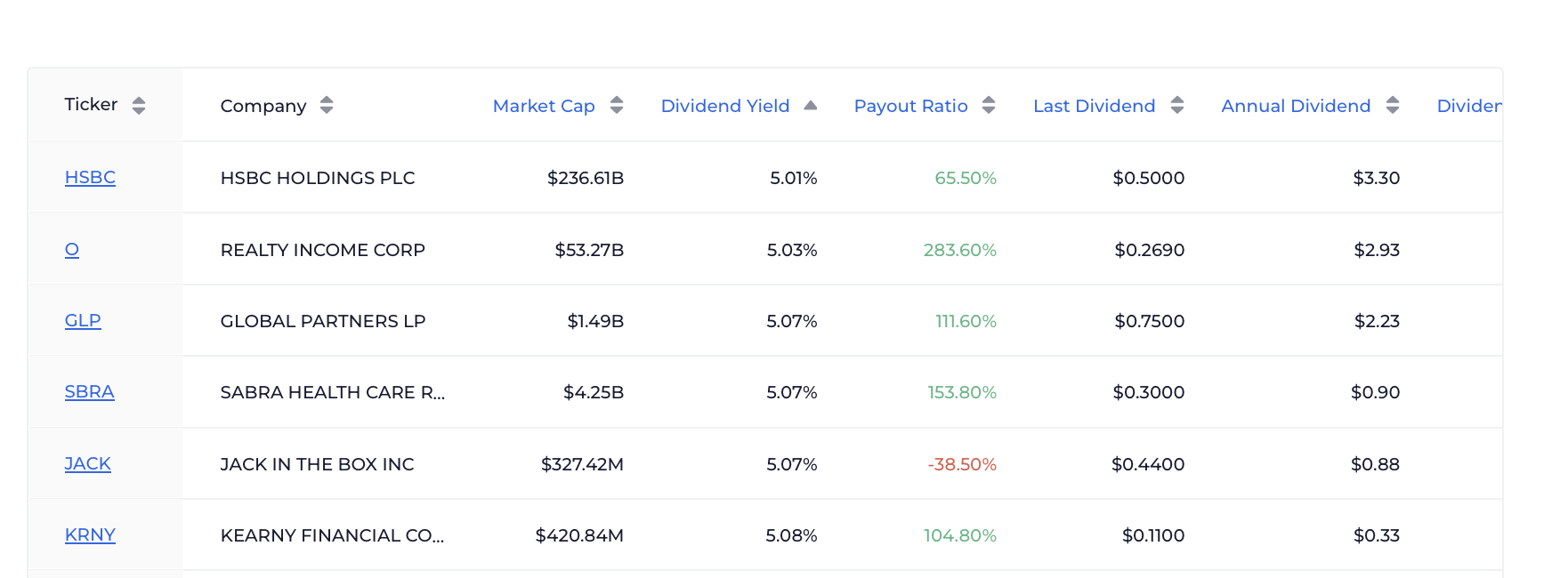
But don’t worry. You don’t actually have to do the math for yourself. With tools like WallStreetZen’s screeners, you can automatically filter on dividend yield:
What Makes a Good Dividend Yield?
As of 2025, here are general guidelines for evaluating dividend yields, though these ranges can shift based on market conditions:
- 2-4%: Generally considered reasonable for established blue-chip companies
- 4-6%: Attractive yields that warrant closer investigation
- 6%+: High yields that require careful analysis — could indicate opportunity or risk
Keep in mind that these are guidelines, not hard rules. When risk-free rates fall, fair yields compress; when rates/risk rise, even high-quality payers can screen at 5–7%+.
A word of caution…
I’ve learned to be cautious with extremely high yields (8%+) because they often signal underlying problems. A 10% yield might look attractive, but if the stock price has fallen 50% due to business troubles, that high yield could be unsustainable.
Dividend Payout Ratio: Measuring Sustainability
While dividend yield tells you how much income you’ll earn, the payout ratio reveals whether those dividends are sustainable.

Calculating the Payout Ratio
Payout Ratio = Dividends Per Share ÷ Earnings Per Share
Alternatively: Payout Ratio = Total Dividends Paid ÷ Net Income
For example, if a company earns $4.00 per share and pays $1.60 in dividends, the payout ratio is 40% ($1.60 ÷ $4.00 = 0.40).
Interpreting Payout Ratios
Here’s how I evaluate payout ratios across different scenarios:
- 30-50%: Generally healthy, leaves room for growth.
- 50-70%: Moderate, acceptable for mature companies.
- 70%+: Higher risk, limited room for increases.
- Over 100%: Red flag — company paying more than it earns.
Different industries have different payout ratio norms. Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) require special attention — instead of using earnings per share, you should calculate payout ratios using Funds From Operations (FFO) or Adjusted Funds From Operations (AFFO), as REITs are required to distribute 90% of taxable income, not net income.
Important Caveats
- Cash flow matters: Dividends are paid out of cash, not accounting earnings. That’s why many investors prefer to calculate the payout ratio using Free Cash Flow (FCF) — the cash left after a company pays its operating expenses and capital investments.
- Temporary spikes: Sometimes a payout ratio looks unsustainably high (even over 100%) because of one-time events such as write-offs or an unusually weak earnings year. Always check multi-year averages to see the true pattern.
Dividend Growth Investing vs. High-Yield Dividend Investing
As you develop your dividend investing strategy, you’ll need to choose between two primary approaches: dividend growth investing and high-yield dividend investing.
Dividend Growth Investing
This approach focuses on companies that consistently increase their dividend payments over time, even if their current yields are modest.
Characteristics:
- Lower initial yields (2-4%).
- Strong dividend growth rates (5-10% annually).
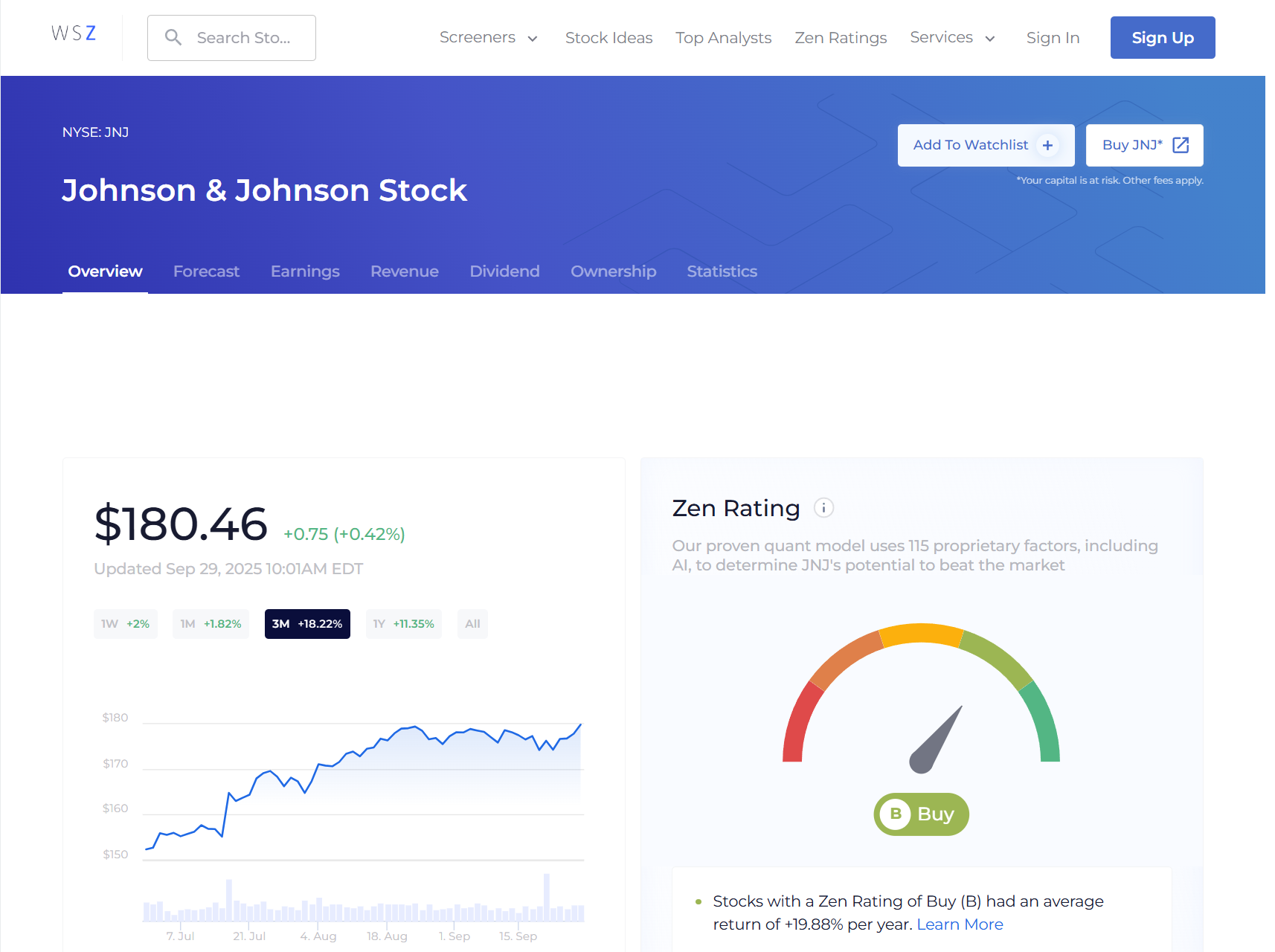
Examples: Companies like Johnson & Johnson (NYSE: JNJ) and Procter & Gamble (NYSE: PG) have increased their dividends for decades. And as you can see below, JNJ isn’t just a dividend delivery service — at writing, it has a Zen Rating of B (Buy), indicating it has solid fundamentals that could lead to long-term growth (B-rated stocks in our system have historically delivered 19.88% returns).
High-Yield Dividend Investing
This strategy targets stocks with immediately attractive dividend yields, prioritizing current income over growth.
Characteristics:
- Higher current yields (4-8%+).
- May have slower or inconsistent dividend growth.
Examples: Utility companies like Eversource Energy (NYSE: ES) or REITs often fall into this category.
What’s the Best Approach For Dividend Investing?
I recommend a blended approach for most investors.
If you’re younger and focused on long-term wealth building, emphasize dividend growth stocks. If you’re closer to or in retirement and need current income, incorporate more high-yield positions while maintaining some growth-oriented dividend stocks.
Dividend Aristocrats: The Gold Standard
The S&P 500 Dividend Aristocrats are those companies in the S&P 500 that have increased their dividends for at least 25 consecutive years (plus meeting size and liquidity criteria). While no index guarantees perfection, Aristocrats represent a subset of firms with a long history of dividend discipline and resilience through multiple business cycles.
Top Dividend Aristocrats for [wpdst-year]
Here are examples of different types of standout Dividend Aristocrats:
- Energy Company with Solid Cash Flow — ExxonMobil (NYSE: XOM): Offers current yield and cash flow generation. However, use multi-year FCF payout ratios rather than earnings alone, since energy cash flows are known to fluctuate with oil prices.
- Essential Products Company — Procter & Gamble (NYSE: PG): A consumer goods company with 69 years of consecutive dividend increases. P&G makes products people buy regardless of economic conditions.
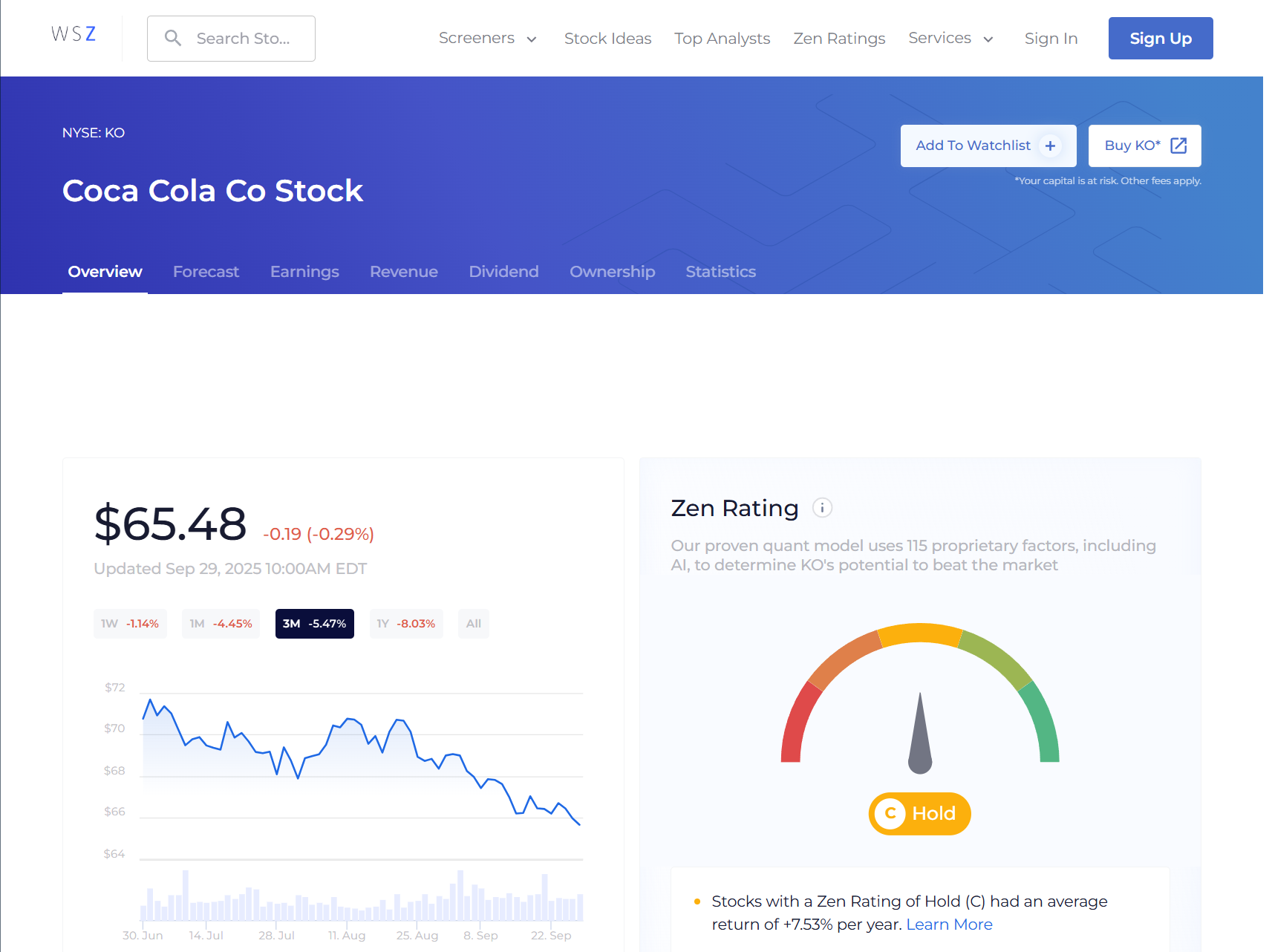
- Global Brand — Coca-Cola (NYSE: KO): The dividend growth story with 63 years of consecutive increases. Coca-Cola’s worldwide brand creates reliable dividend payments.
Monthly Dividend Stocks: Creating Consistent Cash Flow
While most dividend stocks pay quarterly, monthly dividend stocks can provide more consistent cash flow for investors seeking regular income.
Types of Monthly Dividend Stocks
- Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs): Many REITs pay monthly dividends, including Realty Income (NYSE: O), which calls itself “The Monthly Dividend Company.”
- Business Development Companies (BDCs): These companies lend to small and medium-sized businesses and often pay monthly distributions.
- Dividend-Focused ETFs: Some ETFs are structured to pay monthly distributions by holding portfolios of dividend-paying stocks.
How to Build a Monthly Income Stream With Dividends
To create consistent monthly income, you can either invest in monthly dividend stocks or stagger your quarterly dividend stocks so you receive payments every month.
The staggered approach means buying stocks that pay dividends in different months. For example:
- Stock A pays dividends in January, April, July, October
- Stock B pays dividends in February, May, August, November
- Stock C pays dividends in March, June, September, December
This way, you receive dividend payments every month even though each individual stock only pays quarterly.
I prefer the staggered approach because it gives you access to higher-quality companies while still achieving monthly cash flow.
How to Find Dividend Stocks on WallStreetZen
Finding quality dividend stocks requires the right screening tools. WallStreetZen offers several powerful resources to help you identify the best dividend investment opportunities.
WallStreetZen’s Dividend Screeners
Pro Tip: WallStreetZen’s dividend screeners can help you quickly identify high-quality dividend stocks based on your specific criteria.
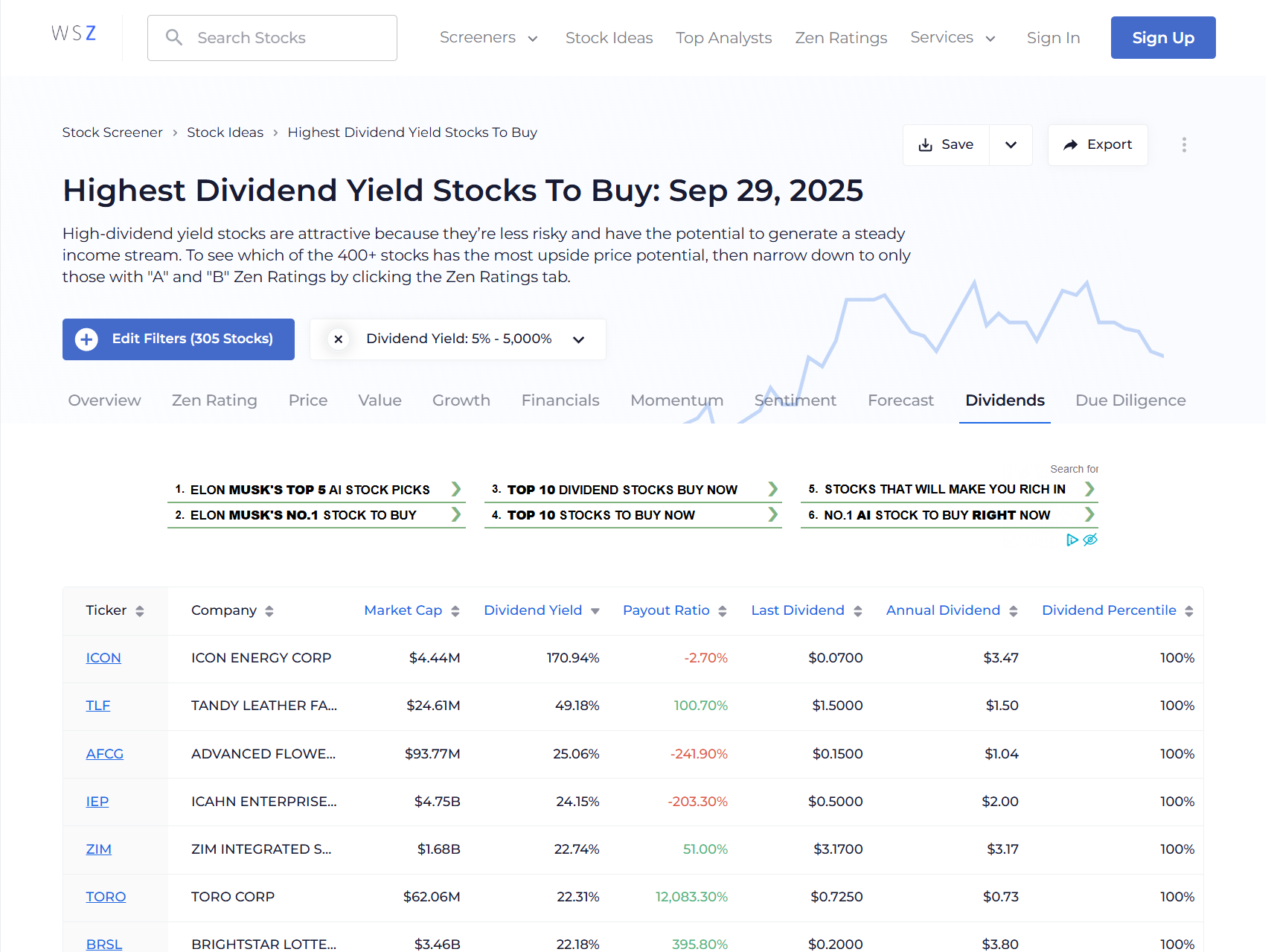
Highest Dividend Yield Stocks Screener: This tool ranks stocks by current dividend yield, helping you identify high-income opportunities. However, always combine yield screening with fundamental analysis to avoid dividend traps.
Dividend Stocks Screener: A comprehensive tool that allows you to filter stocks based on dividend yield, payout ratio, dividend growth rate, and other key metrics.
General Stock Screener: You can customize this screener to focus specifically on dividend criteria, adding filters for minimum yield, maximum payout ratio, and other dividend-related metrics.
How I Use These Screeners Effectively
When I use WallStreetZen’s tools, I follow a systematic approach:
- Start Broad: Begin with the dividend screener, setting minimum yield requirements (typically 2.5%+).
- Add Quality Filters: Include maximum payout ratios (usually under 80%) and minimum market capitalizations.
- Focus on Growth: Review individual stock profiles to check historical dividend growth and stability over 5+ years.
- Analyze Fundamentals: Use WallStreetZen’s detailed stock analysis, Zen Ratings, and financial health metrics to evaluate each candidate’s overall quality.
Building Your Dividend Investment Strategy
Creating a successful dividend investing strategy requires more than just buying high-yield stocks. Here’s my framework for building a sustainable dividend portfolio.
Step 1: Define Your Goals
Before selecting stocks, clarify what you want from dividend investing:
Current Income Focus: Target higher-yielding stocks (4-6%) with sustainable payout ratios.
Long-Term Wealth Building: Emphasize dividend growth stocks with lower current yields.
Balanced Approach: Combine both strategies.
Step 2: Diversify Across Sectors
Don’t concentrate your dividend investments in one industry. I recommend spreading investments across:
- Consumer Staples: Companies like Procter & Gamble (NYSE: PG) and Coca-Cola (NYSE: KO).
- Healthcare: Dividend Aristocrats like Johnson & Johnson (NYSE: JNJ) and AbbVie (NYSE: ABBV).
- Utilities: Stable dividend payers like Eversource Energy (NYSE: ES).
- Industrials: Companies like 3M (NYSE: MMM) and Emerson Electric (NYSE: EMR).
- Real Estate (REITs): For higher yields and real estate exposure like Realty Income (NYSE: O).
Step 3: Implement Dollar-Cost Averaging
Rather than investing a lump sum, consider dollar-cost averaging by investing a fixed amount regularly. This helps smooth out market volatility.
Step 4: Use Sector-Appropriate Metrics
Different sectors require different analysis approaches:
REITs and BDCs: Focus on AFFO/FFO payout ratios, debt-to-EBITDA (Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation, and Amortization), interest coverage, and debt maturity profiles rather than traditional earnings metrics.
Cyclical Industries (Energy/Materials): Analyze free cash flow payout ratios across business cycles, breakeven prices, and balance sheet resilience during downturns.
Non-REIT/BDC Corporates: Target FCF payout ≤60–70%, net debt/EBITDA, and interest coverage for traditional dividend-paying companies.
Step 5: Monitor and Rebalance
Dividend investing isn’t “set it and forget it.” Regularly review your holdings for:
- Changes in dividend policy.
- Deteriorating financial metrics.
- Better opportunities in your target sectors.
Dividend Reinvestment: Accelerating Wealth Building
One of the most powerful tools in dividend investing is the Dividend Reinvestment Plan (DRIP), which automatically uses your dividend payments to purchase additional shares.
How DRIPs Work
Instead of receiving cash dividends, DRIPs automatically reinvest your dividend payments into additional shares of the same stock. Many brokers offer this service with no fees or commissions.
Common Dividend Investing Mistakes to Avoid
Here are the biggest pitfalls and how to avoid them:
Chasing High Yields
The biggest mistake is assuming higher yields are always better. A 10% yield often signals a company in distress with an unsustainable dividend. Always investigate why a yield is unusually high.
Ignoring Payout Ratios
Never buy a dividend stock without checking its payout ratio. A company paying 90% of its earnings as dividends has little room for error and limited growth potential.
Lack of Diversification
Don’t concentrate holdings in one sector, even if it’s traditionally dividend-friendly. The 2008 financial crisis showed how quickly “safe” dividend sectors can cut payouts.
Final Word
Dividend investing offers a proven path to building wealth while generating passive income. By focusing on quality companies with sustainable dividend policies, you can create a portfolio that pays you while potentially appreciating in value.
Remember, successful dividend investing isn’t about chasing the highest yields — it’s about finding companies with strong competitive positions, reasonable payout ratios, and commitment to returning cash to shareholders. Use WallStreetZen’s screeners to identify candidates, but always perform thorough fundamental analysis.
Start with small positions, diversify across sectors, reinvest your dividends, and maintain a long-term perspective. With patience and discipline, dividend investing can become a cornerstone of your wealth-building strategy.
The key is getting started. Even small, consistent investments in quality dividend stocks can grow into substantial passive income streams over time.
FAQs:
Is dividend investing worth it?
Yes, dividend investing can be highly worthwhile for many investors. Dividend stocks have historically provided competitive total returns while offering reduced volatility compared to non-dividend stocks.
The combination of regular income plus potential capital appreciation makes dividend investing particularly attractive for investors seeking current income or building long-term wealth.
However, success requires focusing on quality companies with sustainable dividend policies rather than simply chasing high yields.
What is a good dividend for stocks?
A "good" dividend depends on your investment goals and the company's industry. Generally, dividend yields between 2-6% are considered reasonable for most established companies.
More important than absolute yield is dividend sustainability — look for payout ratios under 80%, consistent dividend growth history, and strong underlying business fundamentals.
A 3% yielding stock that grows dividends 8% annually may be better than a 6% yielder with no growth potential.
How much does it take to make $1000 a month in dividends?
To generate $1,000 monthly ($12,000 annually) in dividend income, you need to divide $12,000 by your portfolio's average dividend yield. With a 4% average yield, you'd need $300,000 invested ($12,000 ÷ 0.04). With a higher 5% yield, you'd need $240,000.
Remember that building this takes time — through consistent investing, dividend reinvestment, and compound growth, even modest initial investments can eventually generate substantial monthly income.
Are dividends a good way to invest?
Dividends can be an excellent investment approach, especially for investors seeking current income, lower volatility, or inflation protection. Dividend-paying companies tend to be more established and financially stable, providing some downside protection during market turbulence.
However, dividend investing works best as part of a diversified portfolio rather than as your only investment strategy. Young investors focused purely on growth might prefer to emphasize non-dividend stocks initially.
What are the 5 highest dividend paying stocks?
As of 2025, some of the highest-yielding dividend stocks include various REITs, utilities, and energy companies, though specific yields change with stock prices.
Rather than focusing solely on the highest yields, I recommend screening for sustainable high-yield stocks with reasonable payout ratios and strong business fundamentals.
Use WallStreetZen's dividend screeners to identify current high-yield opportunities while analyzing each company's dividend sustainability and growth prospects.
Where to Invest $1,000 Right Now?
Did you know that stocks rated as "Buy" by the Top Analysts in WallStreetZen's database beat the S&P500 by 98.4% last year?
Our March report reveals the 3 "Strong Buy" stocks that market-beating analysts predict will outperform over the next year.